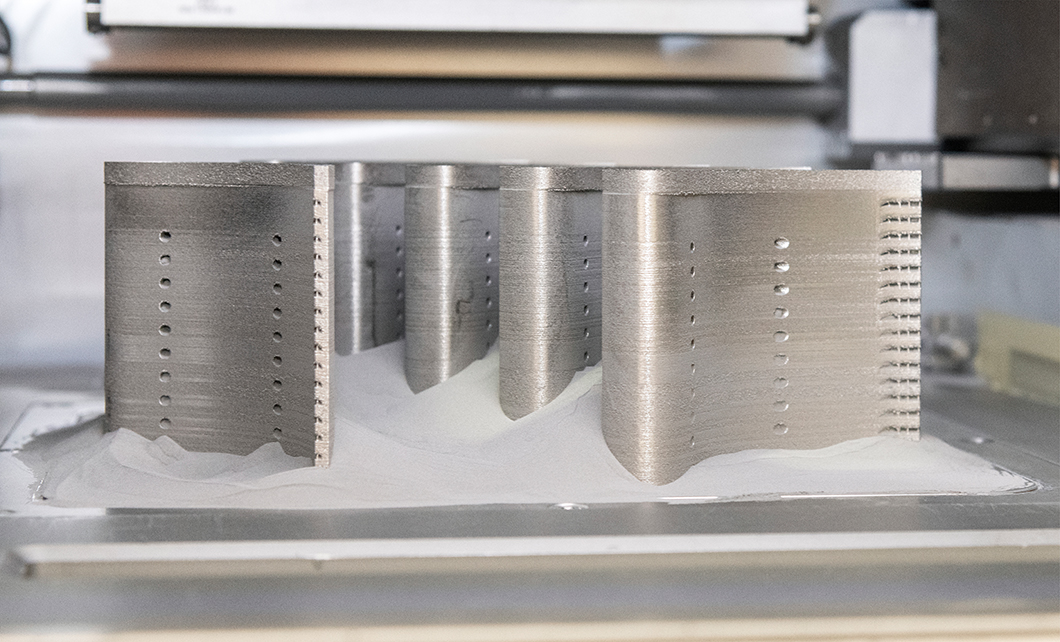
Additive manufacturing of turbine blades from a nickel base superalloy
Source: BAM
Project period
01/01/2023 - 30/06/2025
Project type
Collaborative research project
Project status
Ongoing
Description
The aim of the project HTA 2.0 (2nd phase) - Sustainable Additive Manufacturing for High Temperature Applications - is to increase the usability and sustainability of additively manufactured high-temperature components in gas turbine industry.
Location
Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM)
Unter den Eichen 87
12205 Berlin
HTA 2.0 - High Temperature Applications
Challenge
The project HTA 2.0 - Sustainable Additive Manufacturing for High-Temperature Applications directly follows the successful first project phase of HTA 2.0 - High-Temperature Applications. In the second funding period, the portfolio of AM technologies for gas turbine components will be expanded by two additional processes, this time with a focus on faster and more efficient processes. New strategies for the post-processing of components produced by powder bed based additive manufacturing (AM) will close the loop with the main aim of reducing material waste and minimising process times. The result will be an overall view of which AM technology is more sustainable for which component as a whole. In the end, it is not a matter of adapting the component to the technology, but vice versa.
Objectives
The research project aims to evaluate additive manufacturing processes in the context of sustainable product development and to identify more economically and ecologically efficient component solutions for the area of high temperature gas turbine components. The increase in material reusability and the exploitation of previously unexploited potentials of additive manufacturing processes, as well as the improvement of post-processing strategies and procedures, should contribute to this. To achieve this, material, production and design must be optimally harmonised and targeted digitalisation solutions must be integrated into product development.
Method
In order to be able to evaluate additively manufactured components for high-temperature applications in the context of sustainable product development, it is important to have extensive knowledge about the processability of high-temperature materials, the interaction between product design, manufacturing process and post-treatment, as well as the behaviour of the materials in application. BAM contributes to this with its expertise in comprehensive material characterisation, additive manufacturing process, process monitoring and determination of material behaviour at high temperatures.

View into the Laser Powder Bed Fusion process
Source: BAM
BAM's contribution
Quality assurance of AM components by means of CT
BAM Department Micro Non-Destructive Testing, Dr. Tobias Fritsch
Mechanical-technological long-term behaviour of AM components
BAM Department Materials Modelling, Dr. Bernard Fedelich
Process parameter development for the DED-Arc/M process
BAM Department Welding Technology, Dr. Andreas Pittner
Influences of preheating on the PBF-LB/M process and the resulting properties
BAM Department Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Components, Dr. Gunther Mohr
Influences of the PBF-LB/M process on powder degradation
BAM Department Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Components, Dr. Gunther Mohr
Process development of electron beam welding of AM components
BAM Department Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Components, Dr. Gunther Mohr
Residual stress analysis of AM components
BAM Department Weld Mechanics, Dr. Arne Kromm
Project coordination
Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM)
Division Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Components
Partners
Siemens Energy Global GmbH & Co. KG
Technische Universität Berlin (verschiedene Lehrstühle)
Fraunhofer IPK (Fraunhofer-Institut für Produktionsanlagen und Konstruktionstechnik)
Funding
The project is carried out within the Werner-von-Siemens Centre for Industry and Science. It is funded by the Investitionsbank Berlin (ProFIT) and co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF).

Logo of the Werner-von-Siemens Centre for Industry and Science
Source: WvSC

Logo of the EU European Regional Development Fund
Source: EU


