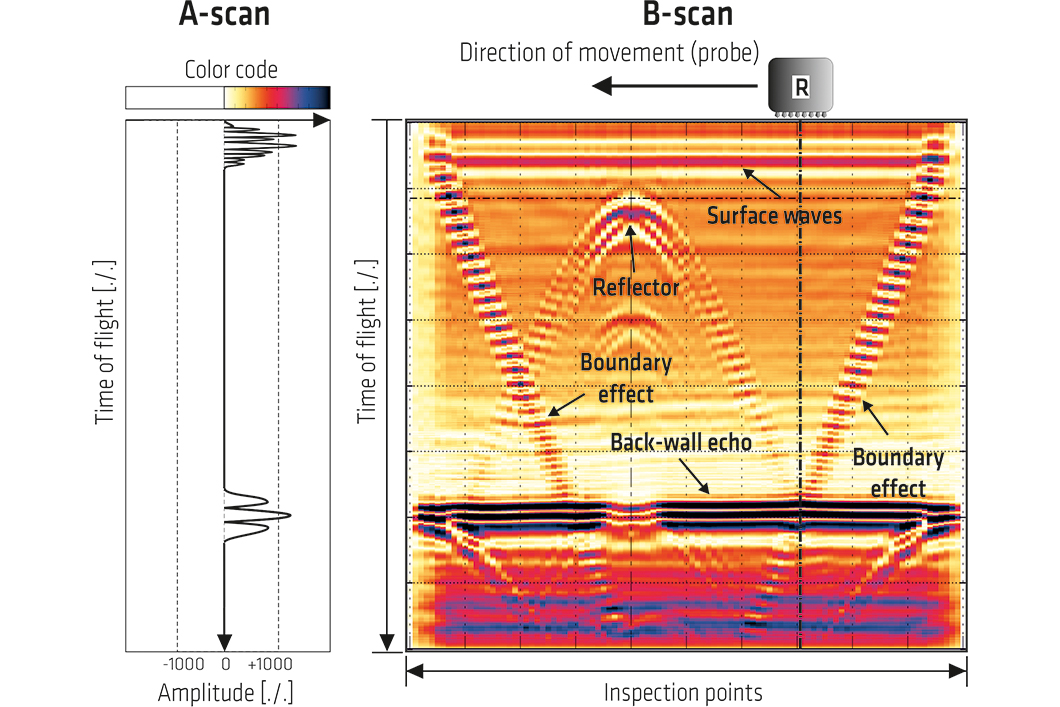
Ultrasonic image (A-, B-scan) of the reference data set on a test specimen made of polyamide
Source: BAM, division Non-destructive Testing Methods for Civil Engineering
The evaluation of technical components and materials in terms of condition and quality with the aid of non-destructive testing methods plays an outstanding role both in industrial series production and in the individual assessment of components. The ultrasonic echo method is used for a wide variety of testing tasks, such as measuring the thickness of a component. The safe application of the test method requires on the one hand a high qualification of the user. On the other hand, the performance of the test method needs to be proven in extensive test scenarios. An important component for this is the correct interpretation of the measurement data by the operator. In particular, the testing of concrete in the construction industry poses a special challenge here, since every concrete mixture has different material properties. In addition, the test conditions on the construction site, such as accessibility to the component, differ significantly. This can lead to different operators obtaining different results from the same test scenario.
At the Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM) in Berlin, among other things, test methods are developed and their performance is demonstrated. For this purpose, references such as materials, test procedures or data sets are generated, which are used to evaluate these developed test methods. An important component of these references are data sets that are created according to the BAM Data Policy and made available to the scientific community and users of test methods in practice on the basis of the FAIR principles (Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, and Reuse).
The published data set is ultrasonic data. The investigated specimen consists of the isotropic homogeneous material polyamide. The surface of the specimen is scanned in a point grid by an automatic scanner system. The value of the data set for users of the test method is that a number of common building materials such as concrete have a highly heterogeneous structure, which leads to strong sound attenuation due to the scattering and absorption of the ultrasonic signal. Volume scattering does not occur in an isotropic homogeneous material such as polyamide. Further the specimen has a high industrial machining quality and ensures a very high accuracy regarding the geometrical dimensions.
Different stakeholders can benefit from the dataset. It is possible to compare the results of different reconstruction algorithms using the dataset (e.g. in round robin tests). Furthermore, the effects of varying input parameters in a reconstruction calculation can be analysed. In addition, using the experience gathered with the presented dataset, additional test specimens and datasets can be developed and acquired for different testing scenarios.
Low frequency ultrasonic dataset for pulse echo object detection in an isotropic homogeneous medium as reference for heterogeneous materials in civil engineering
Stefan Maack, Stefan Küttenbaum, Benjamin Bühling, Ernst Niederleithinger
published in Data in Brief, Vol. 42, article no. 108235, pages 1 - 11, 2022
BAM department Non-destructive Testing division Non-destructive Testing Methods for Civil Engineering


