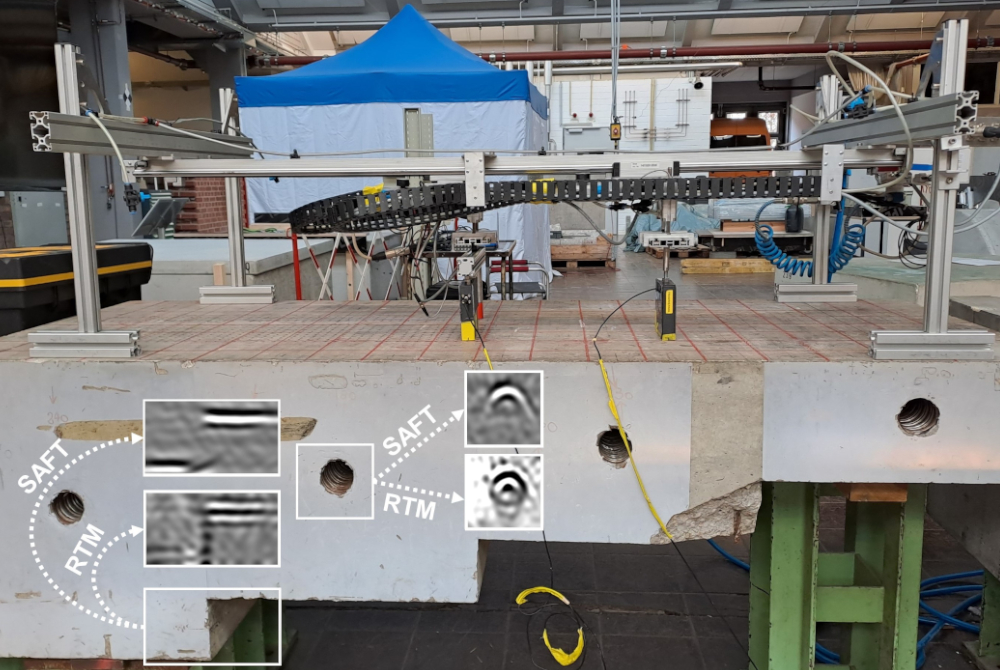
Ultrasonic measurements on a concrete specimen and imaging results from SAFT and RTM, exemplarily shown for one step and tendon duct
Source: BAM
The ultrasonic echo technique is widely used in non-destructive testing (NDT) to inspect concrete structures and is commonly applied for tasks such as measuring thickness, determining geometry, and locating embedded components like tendon ducts. To improve imaging of complex geometries in concrete, a seismic imaging algorithm from geophysics Reverse-Time Migration (RTM) – was adapted for the inspection of concrete objects. Unlike traditional imaging algorithms, such as the Synthetic Aperture Focusing Technique (SAFT), RTM can effectively process all wavefield phenomena, including primary and multiple reflections, making it ideal for challenging structures. This study focuses on applying and evaluating a two-dimensional (2D) elastic RTM algorithm that specifically addresses horizontally polarized shear (SH) waves, which are predominantly used in ultrasonic NDT of concrete. The 2D elastic SH RTM algorithm was applied for validation to SH-wave ultrasonic data collected from a concrete specimen with a complex back wall geometry and four tendon ducts - features frequently encountered in real-world NDT scenarios. The results obtained in this study show that by using elastic SH RTM nearly all structural elements within the concrete specimen were successfully reproduced. Specifically, the following advancements were achieved:
- The imaging of all vertical reflectors within the concrete specimen, including those along the back wall and lateral edges - an outcome that was not possible with conventional SAFT imaging.
- The complete imaging of the circular cross-sections of the tendon ducts, whereas SAFT could only reconstruct the top edges of these built-in components.
- The determination of the diameters of the tendon ducts - a level of detail that is unattainable with SAFT imaging.
These advancements for ultrasonic imaging of concrete structures are unique, as no previous studies have achieved such detailed imaging of tendon duct cross-sections and challenging back wall geometries. Elastic SH RTM significantly enhances the imaging of structural features in concrete and offers new possibilities for ultrasonic inspection and maintenance of critical infrastructure. The RTM work was conducted as part of the BAM-PhD program „Menschen-Ideen“ and follow-up projects. The original RTM code, developed in collaboration with the Colorado School of Mines, has been continuously improved and extended here.
Application of iterative elastic reverse time migration to shear horizontal ultrasonic echo data obtained at a concrete step specimen
Maria Grohmann, Ernst Niederleithinger, Christoph Büttner, Stefan Buske
Near Surface Geophysics, Volume 22, Issue 5, 2024


